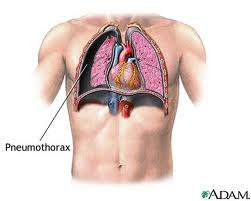
Pathophysiology and Etiology
- Spontaneous pneumothorax due largely located superficial bullae rupture, and preceded by an increase in intra-pulmonary pressure, among others: cough hard or after blowing musical instruments, sneezing, straining, and others. The entry of air into the pleural cavity, through a tear in the visceral pleura. Bula congenital, predisposing especially in young males. Bula may also arise due to pulmonary tuberculosis, pneumoconiosis and bronchial obstruction.
- Traumatic pneumothorax can be caused by a "penetrating and non penetrating injury," either with or without rib fractures.
- "Surgical trauma" and "iatrogenic damage". Surgery can cause this type of pneumothorax.
- "Artificial pneumothorax" necessary for the treatment of hemoptysis in pulmonary tuberculosis as well as diagnostic measures for lung tumors.
- "Tension pneumothorax" due to "check valve" mecanism, so that air can enter but can not get out of the pleural cavity to the mediastinum due to a healthy one side driven.
- Open pneumothorax, occurs when the visceral pleura remains torn open so that the pressure in the pleural cavity with the outside air pressure.
- Closed pneumothorax, when ripping a hole closes after the incoming air is quite a lot. As a result the pressure in the pleural cavity is higher than the outside air pressure.
- Hemopneumothoraks, hidropneumothoraks and piopneumothoraks, when the pleural cavity contains blood, pleural fluid or pus clear.
Symtoms and Clinical Examination
- Sudden chest pain
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Respiratory failure and may be accompanied by cyanosis Puls.
- There is often a "Circulatory collapse" because of "Tension pneumothorax".
- In the percussion sound obtained hipersonor
- On auscultation, decreased breath sounds found on the side until the pain disappears.
Chest X-ray Pictures
1. On PA X-ray chest images visible edge of a collapsed lung in the form of a line. In pneumothorax parsialis the localization in the anterior or posterior, the perimeter of the lung may not be visible.
2. "Mediastinal shift" can be seen in the photograph Anatotomical Pathology or fluoroscopy when the patient inspiration or expiration, especially can occur in "Tension pneumothorax".
Differential Diagnosis
1. Pleurisy and pericarditis
2. Myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism
3. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema
4. "Diaphragmatic herniae"
5. "Dissecting aneurysmae aortae".
Indication-specific treatment:
1. "Tension pneumothorax"
2. Pneumothorax accompanied by shortness of breath.
3. Bilateral pneumothorax
4. Large pneumothorax. When a line edge of a collapsed lung> 1 / 3 transverse diameter.
5. There appear to pleural fluid accumulation are aplenty
6. Pneumothorax as a complication of pulmonary diseases, such as supurativa pneumonia, tuberculosis.
7. Recurrent pneumothorax
8. Complications in the use of a ventilator.
Procedure and Management Of Pneumothorax
Complications
- "Tension pneumothorax" will berakhur fatal, if there is "Circulatory collapse".
- Respiratory failure.
- Hemopneumothrax
- Secondary infections
- Pleural thickening
- Atelectasis
- Recurring. 20% in simple or pneumothraks pneumothraks simplex and 50% in patients with COPD
- Mediastinal emphysema
- "Re-expansion pulmonary oedema".
- Good, if immediate relief and intensive treatment, especially regarding healthy young patients.
- Essentially dependent disease or "underlying disease", is very dangerous when the patient with COPD.
Reference
- Crofton J, Douglas A. Respiratory Disease, 3rd edition . Blackwell Scientific Publications, Singapore, 1984, pp. 541 – 546.
- Graham K, Crompton. Diagnosis and Management of Respiratory Diseases. Blackwell Scientific Publications. Oxford-London- Edinburg 1980, p. 150 – 163.
- Sol Katz. Spontaneus Pneumothorax In : Respiratory Emergency. Ed. By Moser KM, Spragg, R.G, 2nd edition. The CV Mosby Company, London, 1982, p. 176 – 193.
Tags : tension pneumothorax, spontaneous pneumothorax, spontaneous, pneumothorax symptoms, pneumothorax treatment , open pneumothorax, pneumothorax symptoms, symptoms of pneumothorax, pneumothorax definition, right pneumothorax, pneumothorax causes, pneumothorax, what is pneumothorax, Hemopneumothrax
I started on COPD Herbal treatment from Ultimate Health Home, the treatment worked incredibly for my lungs condition. I used the herbal treatment for almost 4 months, it reversed my COPD. My severe shortness of breath, dry cough, chest tightness gradually disappeared. Reach Ultimate Health Home via their email at ultimatehealthhome@gmail.com . I can breath much better and It feels comfortable!