Definitions
 Edema
Edema, in general, means swelling. This typically occurs when fluid from the inside of blood vessels leak out of blood vessels into surrounding tissues, causing swelling. This can occur because of too much pressure in blood vessels or there is not enough proteins in the blood stream to hold the liquid in the plasma (part of blood that does not contain any blood cells).
Pulmonary Edema is the term used when edema occurs in the lungs. The area immediately outside of the small blood vessels in the lung occupied by air pockets are very small, called alveoli. This is where oxygen from the air through which blood is taken by, and carbon dioxide in the blood released into the alveoli to exhaled out. Normal alveoli have very thin walls that allow air exchange, and liquids are usually kept away from the walls of the alveoli-dindig unless it loses its integrity.
Pulmonary edema is an accumulation of fluid in the lungs due to sudden increase in intravascular pressure.
Pulmonary edema is due to the flow of fluid from the blood into the space next to interstisial pulmonary alveoli of the lungs, exceeding the liquid back into the blood stream or through lymphatic channels.
Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by excess fluid in the lungs. This fluid collects in the air sacs in the lungs of many, making it difficult to breathe. In most cases, heart problems cause pulmonary edema. But fluid can accumulate due to other reasons, including pneumonia, exposure to certain toxins and drugs, and sports or live at high altitude.
Pulmonary edema is the term used when edema occurs in the lungs.
Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by excess fluid in the lung.
Causes
1. Imbalance of Starling Forces:
a) Increased pulmonary capillary pressure:
- Increased pulmonary venous pressure in the absence of left ventricular dysfunction (mitral stenosis).
- Increased pulmonary venous pressure secondary because of impaired left ventricular function.
- Increased pulmonary capillary pressure secondary because of increased pulmonary artery pressure (over-perfusion pulmonary edema).
b) Decrease in plasma oncotic pressure.
- Hypoalbuminemia secondary because of kidney disease, liver, protein-losing enteropaday, dermatological diseases or nutritional diseases.
c) Increased negative pressure intersisial:
- Taking too fast pneumothorax or pleural effusion (unilateral).
- A highly negative pleural pressure due to acute airway obstruction in conjunction with an increase in end-expiratory volume (asthma).
d) Increased oncotic pressure intersisial.
- Until now there has been no example of a trial or clinic.
2. Changes in alveolar-capillary membrane permeability (Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome)
a) Pneumonia (bacteria, viruses, parasites).
b) The material inhaled toxic (phosgene, ozone, chlorine, smoke, Teflon ®, NO2, etc.).
c) Foreign material in the circulation (snake venom, bacterial endotoxins, alloxan, alpha-naphthyl Thiourea).
d) Aspiration of gastric acid.
e) Acute radiation pneumonitis.
f) Material endogenous vasoactive (histamine, kinin).
g) Disseminated intravascular coagulation.
h) Immunology: hypersensitivity pneumonitis, drug nitrofurantoin, leukoagglutinin.
i) Shock Lung therefore outside the thoracic trauma.
j) Bleeding Acute Pancreatitis.
3. Lymphatic insufficiency:
a) Post Lung Transplant.
b) Lymphangitic carcinomatosis.
c) fibrosing lymphangitis (silicosis).
4. Not known / not clear
a) High Altitude Pulmonary Edema.
b) Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema.
c) Narcotic overdose.
d) Pulmonary embolism.
e) Eclampsia
f) Post cardioversion.
g) Post Anesthesia.
h) Post Cardiopulmonary Bypass.
Classification
Based on the cause, is divided into 2 pulmonary edema, cardiogenic and non-cardiogenic. It is important to know because its treatment is very different. Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema due to Left Heart Terrible any reason. Acute Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema is caused by the presence of Acute Left Heart Sucks. But with the precipitation factors, may occur also in patients with Chronic Left Heart Sucks.
» Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Edema, cardiogenic pulmonary edema is caused by abnormalities in the heart organ. For example, the heart does not work properly as the heart pumps are not good or strong the heart is not pumping anymore.
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema resulting from high pressure in blood vessels of the lungs caused by poor heart function. Congestive heart failure caused by poor cardiac pump function (coming from a variety of causes such as arrhythmias and diseases or weakness of the heart muscle), heart attacks, or heart valves can lead to abnormal accumulation of more than the usual amount of blood in blood vessels of the lungs. This can, in turn, causes the fluid from the blood vessels are pushed out into the alveoli when the pressure is growing.
» Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema is that edema is usually caused by the following:
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). In ARDS, the integrity of the alveoli become compromised as a result of an underlying inflammatory response, and this menurus on a leaky alveoli that can be filled with fluid from blood vessels.
- A potentially serious condition caused by severe infections, trauma, lung injury, inhalation of toxins, lung infections, smoking cocaine, or radiation to the lungs.
- Renal failure and inability to remove fluid from the body can cause a buildup of fluid in blood vessels, resulting in pulmonary edema. In people with advanced kidney failure, dialysis may be necessary to remove excess body fluids.
- High altitude pulmonary edema, which can occur due to a rapid rise to high altitudes over 10,000 feet.
- Traumatic brain, bleeding in the brain (intracranial hemorrhage), severe seizures, or brain surgery can sometimes result in accumulation of fluid in the lungs, causing neurogenic pulmonary edema.
- Lung expanding rapidly can sometimes lead to a re-expansion pulmonary edema. This may occur in cases when a collapsed lung (pneumothorax) or large amounts of fluid around the lungs (pleural effusion) was issued, resulting in rapid expansion of the lung. This can result in pulmonary edema only on the affected side (unilateral pulmonary edema).
- Rarely, overdose on heroin or methadone can lead to pulmonary edema. An overdose of aspirin or the use of high doses of aspirin can lead to chronic aspirin intoxication, especially in the elderly, which may cause pulmonary edema.
- Other causes are less frequent than non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema may include pulmonary embolism (blood clot that had walked into the lungs), acute lung injury related to transfusion or transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), some infections -viral infection, or eclampsia in pregnant women.
Pathophysiology
Pulmonary edema occurs when the alveoli are filled with excess fluid that seeps out of blood vessels in the lungs instead of air. This can cause problems with gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide), resulting in difficulty breathing and poor blood pengoksigenan. Occasionally, this can be referred to as "water in the lungs" when describing this condition in patients. Pulmonary edema can be caused by many different factors. He can be connected in heart failure, called cardiogenic pulmonary edema, or linked to other causes, referred to as non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Clinical Manifestations
The most common symptoms of pulmonary edema is shortness of breath. This is probably a gradual onset if the process develops slowly, or he may have a sudden onset in cases of acute pulmonary edema. Other common symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath develop faster than normal with usual activities (Dyspnea on Exertion), rapid breathing (tachypnea), dizziness, or weakness.
Low blood oxygen levels (hypoxia) may be detected in patients with pulmonary edema. Furthermore, upon examination of the lungs with a stethoscope, the doctor may hear abnormal lung sounds, rales or crackles crate (short boiling sounds disjointed, which corresponds to the muncratan fluid in the alveoli during breathing).
Clinical manifestations Pulmonary Edema specifically also divided into 3 stages:
Stage 1.
The existence of small blood vessels distended and prominent lung would improve gas exchange in lungs and slightly increase the capacity of diffusion of CO gas. Complaints at this stage may just be a shortness of breath while working. Physical examination is also not clearly found abnormalities, except maybe the inspiration for ronkhi at the time of opening of the closed airway during inspiration.
Stage 2.
At this stage intersisial pulmonary edema. Limit pulmonary blood vessels become blurred, so too the hilum also become blurred and interlobularis thickened septa (Kerley B lines). By accumulation of fluid in the loose network of inter-sisial, will further reduce the small airways, especially in the basal area because of the influence of gravity. Might also occur bronkhokonstriksi reflex. Often there is takhipnea. Although this is a sign of impaired left ventricular function, but takhipnea also help pump lymph flow is slowed so that the buildup of fluid intersisial. On examination there was little change in spirometry alone.
Stage 3.
At this stage of alveolar edema. Severely impaired gas exchange, hypoxemia and hypocapnia occur. Patients seem very crowded with reddish frothy cough. Vital capacity and other lung volume decreased markedly. Occurs right-to-left intrapulmonary shunt. Patients usually suffer from hypocapnia, but in severe cases can occur hypercapnia and acute respiratory acidemia. In this situation morphine has to be used with caution (Ingram and Braunwald, 1988).
Pam edema that occurs after acute myocardial infarction is usually due to capillary pulmonary hypertension. However, experiments on dogs that do arteriakoronaria ligation, pulmonary edema occurred despite normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, which can be prevented with indomethacin administration before. It is estimated that by inhibiting cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase or cyclooxygenase to reduce edema 'secondary to increased pulmonary alveolar-capillary permeability; on human beings still requires further research. Sometimes patients with acute myocardial infarction and pulmonary edema, capillary wedge pressure normal lungs; this is probably due to the slow clearance of edema fluid radiographically although pulmonary capillary pressure has gone down or alternatively in some patients an increase in alveolar-capillary permeability secondary lung because of the contents sekuncup low as in cardiogenic shock lung.
Diagnosis Supports
»Physical Examination
- Central cyanosis. Shortness of breath by breath sounds like a frothy mucus.
- Ronchi loud in the basal lung wet and then took up almost the entire lung field, sometimes accompanied by dry and expiratory Ronchi which extends a result of bronchospasm so-called cardiac asthma.
- Tachycardia with S3 gallops.
- Murmur when valve abnormalities.
»Electrocardiography. Can sinus tachycardia with left atrial hypertrophy or atrial fibrillation, depending on the cause of heart failure. Preview infarction, left ventricular hypertrophy or arrhythmias can be found.
»Laboratory
- Low pO2 blood gas analysis, pCO2 initially low and then hypercapnia.
- Enzymes cardiospesific increase if the cause of myocardial infarction.
- Blood routine, urea, creatinine, electrolytes, urinalysis, thoracic images, ECG, cardiac enzymes (CK-MB, Troponin T), coronary angiography.
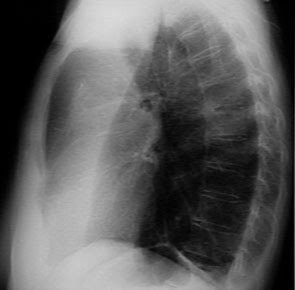
Photo thoracic Pulmonary edema is typically diagnosed by chest X-ray. Radiograph (X-ray) a normal chest consists of a centralized area that offends white heart and major blood vessels plus the bones of the vertebral column, with the lung fields showed as areas darker on each side, which surrounded by the bone structures of the chest wall.
X-ray chest with a typical pulmonary edema may show more white Tampakan in both lung fields than usual. The cases are more severe than pulmonary edema may show opacification (bleaching) is significant in the lung with minimal visualization of the lung fields are normal. Bleaching represents filling of the alveoli as a result of pulmonary edema, but it may provide minimal information about the possible underlying causes.
»Overview Radiology found:
- Widening or thickening of the hilum (hilar vascular dilatation)
- Increased lung pattern (more than 1 / 3 lateral)
- Vascular cranialization
- Bleak hilum (the limit is not clear)
- Interstitial fibrosis (descriptions such as granulomas, small granulomas or miliary nodules)
»Preview the cause of heart failure echocardiography: valve abnormalities, ventricular hypertrophy (hypertension), Segmental wall motion abnormally (CHD), and generally found left ventricular dilatation and left atrium.
»Measurement of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
Other diagnostic tools used in assessing the underlying cause of pulmonary edema include the measurement of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal pro-BNP. This is the marker proteins (hormones) that will arise in the blood caused by the stretching of the heart chambers. The increase of BNP nanograms (a billionth of a gram) per liter larger than a few hundred (300 or more) is very high suggesting cardiac pulmonary edema. On the other hand, the values are less than 100 are essentially rule out heart failure as the cause.
»Pulmonary artery catheter (Swan-Ganz)
Pulmonary artery catheter (Swan-Ganz) is a long, thin tube (catheter) is inserted into large veins of the chest or neck and advanced through the room - right side of the heart chamber and placed into the pulmonary capillaries or pulmonary capillaries (branch -small branches of blood vessels of the lungs). This tool has the ability to directly measure the pressure in the pulmonary vessels, called pulmonary artery wedge pressure. Wedge pressure of 18 mmHg or higher is consistent with cardiogenic pulmonary edema, while wedge pressure of less than 18 mmHg usually support non-cardiogenic cause of pulmonary edema. Swan-Ganz catheter placement and interpretation of data is done only at the intensive care unit (ICU).
Differential Diagnosis
Management
- Semi-Fowler position.
- Oxygen (40-50%) to 8 liters / minute if necessary with a mask.
- If deteriorated (patients increasingly congested, takipneu, Ronchi added, can not be maintained PaO2 ≥ 60 mmHg with O2 concentration and high flow, CO2 retention, hypoventilation, or unable to adequately reduce the edema fluid), then performed endotracheal intubation, suctioning and ventilators.
- Infusion emergency. Monitor blood pressure, ECG monitor, pulse oximetry if available.
- Sublingual or intravenous nitroglycerin. Peroral nitroglycerin 0.4 to 0.6 mg every 50-10 minutes. If the systolic blood pressure> 95 mmHg may be given intravenous nitroglycerin starts dose of 3-5 ug / kg.
- If it does not give satisfactory results it can be given IV Nitroprusid starting dose of 0.1 ug / kg / minute if they do not respond to nitrate, the dose is increased to obtain clinical improvement or until systolic blood pressure of 85-90 mmHg in patients who had had blood pressure normal or can be maintained as long as adequate perfusion to vital organs.
- Morphine sulfate 3-5 mg iv, may be repeated every 25 minutes, a total dose of 15 mg (best avoided).
- Diuretics Furosemide 40-80 mg IV bolus dose may be repeated or increased every 4 hours or continued drip continue to achieve urine output of 1 ml / kg / hour.
- If necessary (blood pressure drop / mark hypoperfusion): Dopamine 2-5 ug / kg / min or dobutamine 2-10 ug / kg / min to stabilize hemodynamics. The dose may be increased according to clinical response or both.
- Thrombolytic or revascularization in patients with myocardial infarction.
- Ventilator in patients with severe hypoxia, acidosis / does not work with oxygen.
- Operations on the complications of acute myocardial infarction, such as regurgitation, VSD, and ventricular wall rupture / corda tendinae.
Tags :
pulmonary edema definition,
pulmonary oedema,
flash pulmonary edema,
acute pulmonary edema,
pulmonary edema symptoms,
pulmonary edema causes,
pulmonary edema treatment,
lung edema,
altitude pulmonary edema,